Posted 04 October 2019,
In my last post I described my Arduino Mega test program to interface with the popular Invensense MPU6050 IMU and it’s GY-521 clone. In this post I describe the interface configuration for using a polling strategy rather than relying on the IMU6050’s interrupt signal. A polling strategy can be very useful as it is much simpler, and saves a pin connection from the MPU6050 to the controller; all that is required is +V, GND, SDA & SCL, as shown below:
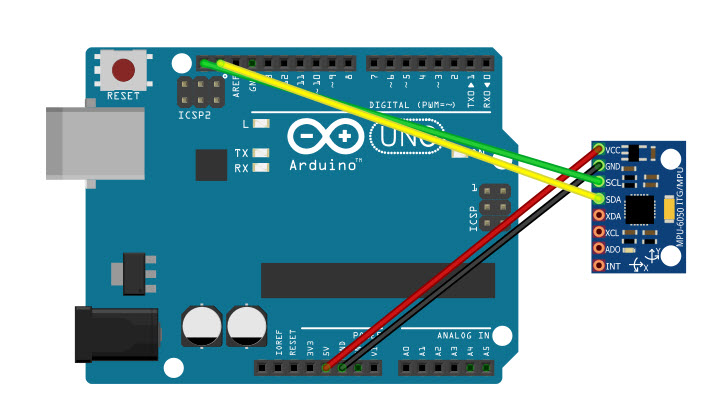
With this wiring setup, the control program is shown below:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 |
/* Name: Arduino MPU6050 Polling Test.ino Created: 10/5/2019 1:31:08 PM Author: FRANKWIN10\Frank This is a complete, working MPU6050 (GY-521) example using polling vs interrupts. It is based on Jeff Rowberg's MPU6050_DMP6_using_DMP_V6.12 example. After confirming that the example worked properly using interrupts, I modified it to remove the need for the interrupt line. */ #include "I2Cdev.h" #include "MPU6050_6Axis_MotionApps_V6_12.h" //changed to this version 10/04/19 #include "elapsedMillis.h" // class default I2C address is 0x68 // specific I2C addresses may be passed as a parameter here // AD0 low = 0x68 (default for SparkFun breakout and InvenSense evaluation board) // AD0 high = 0x69 MPU6050 mpu; //MPU6050 mpu(0x69); // <-- use for AD0 high #define LED_PIN 13 // (Arduino is 13, Teensy is 11, Teensy++ is 6) bool blinkState = false; // MPU control/status vars bool dmpReady = false; // set true if DMP init was successful uint8_t mpuIntStatus; // holds actual interrupt status byte from MPU uint8_t devStatus; // return status after each device operation (0 = success, !0 = error) uint16_t packetSize; // expected DMP packet size (default is 42 bytes) uint16_t fifoCount; // count of all bytes currently in FIFO uint8_t fifoBuffer[64]; // FIFO storage buffer // orientation/motion vars Quaternion q; // [w, x, y, z] quaternion container VectorInt16 aa; // [x, y, z] accel sensor measurements VectorInt16 aaReal; // [x, y, z] gravity-free accel sensor measurements VectorInt16 aaWorld; // [x, y, z] world-frame accel sensor measurements VectorFloat gravity; // [x, y, z] gravity vector float euler[3]; // [psi, theta, phi] Euler angle container float ypr[3]; // [yaw, pitch, roll] yaw/pitch/roll container and gravity vector //extra stuff int IMU_CHECK_INTERVAL_MSEC = 100; elapsedMillis sinceLastIMUCheck; float global_yawval = 0.0; //contains most recent yaw value from IMU int global_fifo_count = 0; //made global so can monitor from outside GetIMUHeadingDeg() fcn // ================================================================ // === INITIAL SETUP === // ================================================================ void setup() { // I2C bus init done in SBWIRE.h Serial.begin(115200); while (!Serial); // wait for Leonardo enumeration, others continue immediately // initialize device Serial.println(F("Initializing MPU6050...")); mpu.initialize(); // verify connection Serial.println(F("Testing device connections...")); Serial.println(mpu.testConnection() ? F("MPU6050 connection successful") : F("MPU6050 connection failed")); // load and configure the DMP Serial.println(F("Initializing DMP...")); devStatus = mpu.dmpInitialize(); // supply your own gyro offsets here, scaled for min sensitivity mpu.setXGyroOffset(220); mpu.setYGyroOffset(76); mpu.setZGyroOffset(-85); mpu.setZAccelOffset(1788); // 1688 factory default for my test chip // make sure it worked (returns 0 if so) if (devStatus == 0) { // Calibration Time: generate offsets and calibrate our MPU6050 mpu.CalibrateAccel(6); mpu.CalibrateGyro(6); mpu.PrintActiveOffsets(); // turn on the DMP, now that it's ready Serial.println(F("Enabling DMP...")); mpu.setDMPEnabled(true); // set our DMP Ready flag so the main loop() function knows it's okay to use it Serial.println(F("DMP ready! Waiting for first interrupt...")); dmpReady = true; // get expected DMP packet size for later comparison packetSize = mpu.dmpGetFIFOPacketSize(); } else { // ERROR! // 1 = initial memory load failed // 2 = DMP configuration updates failed // (if it's going to break, usually the code will be 1) Serial.print(F("DMP Initialization failed (code ")); Serial.print(devStatus); Serial.println(F(")")); } // configure LED for output pinMode(LED_PIN, OUTPUT); sinceLastIMUCheck = 0; //this manages 'other program stuff' cycle //print out column headers Serial.println("MSec\tYawDeg"); } // ================================================================ // === MAIN PROGRAM LOOP === // ================================================================ void loop() { // if programming failed, don't try to do anything if (!dmpReady) return; if (mpu.dmpPacketAvailable()) { global_yawval = GetIMUHeadingDeg(); //retreive the most current yaw value from IMU // blink LED to indicate activity blinkState = !blinkState; digitalWrite(LED_PIN, blinkState); } //other program stuff block - executes every IMU_CHECK_INTERVAL_MSEC Msec //for this test program, there's nothing here except diagnostics printouts if (sinceLastIMUCheck >= IMU_CHECK_INTERVAL_MSEC) { sinceLastIMUCheck -= IMU_CHECK_INTERVAL_MSEC; Serial.print(millis()); Serial.print("\t"); Serial.println(global_yawval); if (global_fifo_count != 0) { Serial.print("FIFO Reset!"); mpu.resetFIFO(); } } } float GetIMUHeadingDeg() { // At least one data packet is available mpuIntStatus = mpu.getIntStatus(); fifoCount = mpu.getFIFOCount();// get current FIFO count // check for overflow (this should never happen unless our code is too inefficient) if ((mpuIntStatus & _BV(MPU6050_INTERRUPT_FIFO_OFLOW_BIT)) || fifoCount >= 1024) { // reset so we can continue cleanly mpu.resetFIFO(); Serial.println(F("FIFO overflow!")); // otherwise, check for DMP data ready interrupt (this should happen frequently) } else if (mpuIntStatus & _BV(MPU6050_INTERRUPT_DMP_INT_BIT)) { // read all available packets from FIFO while (fifoCount >= packetSize) // Lets catch up to NOW, in case someone is using the dreaded delay()! { mpu.getFIFOBytes(fifoBuffer, packetSize); // track FIFO count here in case there is > 1 packet available // (this lets us immediately read more without waiting for an interrupt) fifoCount -= packetSize; } global_fifo_count = mpu.getFIFOCount(); //should be zero here // display Euler angles in degrees mpu.dmpGetQuaternion(&q, fifoBuffer); mpu.dmpGetGravity(&gravity, &q); mpu.dmpGetYawPitchRoll(ypr, &q, &gravity); } float yawval = ypr[0] * 180 / M_PI; return yawval; } |
In the above program, the interrupt service routine (ISR) and the accompanying ‘attachInterrupt()’ setup function have been removed as they are no longer needed for the polling arrangement. Instead, the program calls ‘mpu.dmpPacketAvailable()’ every time through the loop, and if a packet is available, GetIMUHeadingDeg() is called to read the packet and return a yaw value. The rest of the code in the loop() function is the place holder for the ‘other stuff’ that the program does when it isn’t paying attention to the IMU.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 |
//other program stuff block - executes every IMU_CHECK_INTERVAL_MSEC Msec //for this test program, there's nothing here except diagnostics printouts if (sinceLastIMUCheck >= IMU_CHECK_INTERVAL_MSEC) { sinceLastIMUCheck -= IMU_CHECK_INTERVAL_MSEC; Serial.print(millis()); Serial.print("\t"); Serial.println(global_yawval); if (global_fifo_count != 0) { Serial.print("FIFO Reset!"); mpu.resetFIFO(); } } |
In this test program, I have set this section up to execute every 100 Msec, but in my robot programs I usually set it up for a 200 Msec interval; 5 cycles/sec is plenty fast enough for a wheeled robot that uses only the IMU yaw information for turn management.
So far, this arrangement seems very stable; I have been running it now for several hours without a hiccup.
Stay tuned,
Frank
Hello, could you please explain to me what the global_fifo_count is doing? Could the FIFO not just be reset directly after the line “global_fifo_count = mpu.getFIFOCount();”?
Max,
The global_fifo_count variable was just there so I could watch the machinery in progress – it’s not needed for an actual implementation. For instance, here are the functions I use in all my projects:
float UpdateIMUHdgValDeg()
{
//Purpose: Get latest yaw (heading) value from IMU
//Inputs: None. This function should only be called after mpu.dmpPacketAvailable() returns TRUE
//Outputs:
// returns true if successful, otherwise false
// IMUHdgValDeg updated on success
//Plan:
//Step1: check for overflow and reset the FIFO if it occurs. In this case, wait for new packet
//Step2: read all available packets to get to latest data
//Step3: update IMUHdgValDeg with latest value
//Notes:
// 10/08/19 changed return type to boolean
// 10/08/19 no longer need mpuIntStatus
// 10/21/19 completely rewritten to use Homer’s algorithm
// 05/05/20 changed return type to float vs bool.
int flag = GetCurrentFIFOPacket(fifoBuffer, packetSize, MAX_GETPACKET_LOOPS); //get the latest mpu packet
if (flag != 0) //0 = error exit, 1 = normal exit, 2 = recovered from an overflow
{
// display Euler angles in degrees
mpu.dmpGetQuaternion(&q, fifoBuffer);
mpu.dmpGetGravity(&gravity, &q);
mpu.dmpGetYawPitchRoll(ypr, &q, &gravity);
//compute the yaw value
IMUHdgValDeg = ypr[0] * 180 / M_PI;
}
return IMUHdgValDeg;//05/05/20 now returns updated value for use convenience
}
uint8_t GetCurrentFIFOPacket(uint8_t* data, uint8_t length, uint16_t max_loops)
{
mpu.resetFIFO();
delay(1);
//int countloop = 0;
fifoCount = mpu.getFIFOCount();
GetPacketLoopCount = 0;
//gl_pSerPort->printf(“In GetCurrentFIFOPacket: before loop fifoC = %d\t”, fifoCount);
while (fifoCount < packetSize && GetPacketLoopCount < max_loops) { GetPacketLoopCount++; fifoCount = mpu.getFIFOCount(); delay(2); } //gl_pSerPort->printf(“In GetCurrentFIFOPacket: after loop fifoC = %d, loop count = %d\n”, fifoCount, GetPacketLoopCount);
if (GetPacketLoopCount >= max_loops)
{
return 0;
}
//if we get to here, there should be exactly one packet in the FIFO
mpu.getFIFOBytes(data, packetSize);
return 1;
}